Book a dental appointment
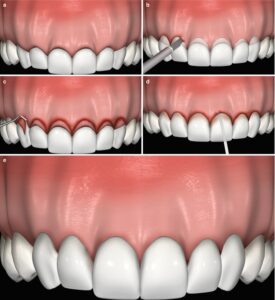
Surgical extension of a crown
What is surgical extension of a crown and when is it necessary?
One indication of this procedure is a situation where during placing a filling or cementing a crown it is revealed that the margin of the healthy dental tissue is located under the gum and it cannot be isolated to avoid exposure of this area to salvia, blood or gingival crevicular fluid. Teeth treated under these conditions have always a higher risk of returning of dental caries.
It is also important that the X-ray shows that between the margin of the prosthesis/filling and the bone ridge there is at least 3–4 mm of healthy dental tissue. If the filling/crown margin is too close to the bone ridge, there will be no room for attachment of soft tissue (it has to adhere to the surface of a tooth root) and the gum in this region remains inflammatory or bone is lost in the area to accommodate the soft tissue zone.
Surgical extension of a crown is also used if during placing a prosthesis it is revealed that there is too little healthy dental tissue to achieve a stabile tooth crown.
Also there is aesthetic indication regarding front teeth (so-called gummy smile) where too much gum is exposed in addition to teeth while smiling.
Surgical extension of a crown
General instructions, after oral surgery
Since there is a risk of bleeding for a week after the surgical intervention, avoid or at least reduce the following during this time:
- Physical exertion (lifting weights, bending forward).
- Visiting a sauna, taking a bath and using a tanning bed, sunbathing, rehabilitation procedures, air travel, long journeys by car.
- Avoid blowing your nose if the doctor said that there was an opening between the oral cavity and the sinus.
- Do not touch the wound with your finger, tongue or any object, do not suck on the wound. Do not put powders, tablets, drops (propolis, tea tree oil) on the wound as this may cause inflammation and bleeding.
- Chew with the other side of the mouth for a few days. Food should be rich in protein, vitamins and minerals and soft, lukewarm or cool. Avoid foods rich in carbohydrates. Harder foods can be eaten when eating them does not cause pain.
- Blood may seep from the wound area for 3–4 days after the operation. The wound will usually start bleeding more 2–3 hours after surgery, as anaesthesia wears off. If bleeding persists, place a sterile gauze swab on the wound for 30 minutes and press the jaws firmly together.
- Keeping an ice pack on the cheek area may reduce swelling.
- Under no circumstances should warm, moist compresses (chamomile, vodka compresses, etc.) be applied to the facial area, as this can cause bleeding and severe swelling.
- Diagnosis
- Objective of periodontitis treatment
- Non-surgical treatment of periodontitis
- Surgical treatment of periodontitis
- Mucogingival surgery
- Side effects of treatment
- When diagnosis and treatment are late
Read more about our other dental treatment services here.
Read more about oral health here.
